Upgrade & Secure Your Future with DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps, MLOps!
We spend hours scrolling social media and waste money on things we forget, but won’t spend 30 minutes a day earning certifications that can change our lives.
Master in DevOps, SRE, DevSecOps & MLOps by DevOps School!
Learn from Guru Rajesh Kumar and double your salary in just one year.
1. Eradicates Business Service Impact
In today’s environment, it’s not enough to know whether or not business services are up and running or down and out. Your company needs to understand the degree to which everything is performing or underperforming, and the availability, health, and status of different business and IT services. Obtaining the depth and level of insight needed to provide the answers is expensive and complicated if you rely on legacy monitoring solutions.
2. Makes Data Analysis Easier
Is your IT department inundated with massive amounts of data in a dizzying array of formats? It can be challenging to stay on top of things using legacy systems not designed to handle the volume and velocity of data common today. To make informed strategic business decisions, you need access to reliable information. But if you don’t have a way to analyze big data, you’ll be at a disadvantage.
3. Get Rid of Application Blind Spots
You’d better hope it’s a planned outage if there’s an application outage. Your company may need to schedule some downtime for routine maintenance, for instance, and your application might not be available for an extended period. In such cases, you’ll want to alert your customers ahead of time so they’re not caught off guard.
4. Get a Handle on the Cloud
As of 2022, north of 60% of all corporate data is stored in the cloud. Reported benefits include, but are not limited to, lower IT costs, scalability, and business continuity. But one of the problems that many companies experience when they enter the cloud is sprawl. In other words, many businesses are working with multiple cloud providers to meet their different requirements.
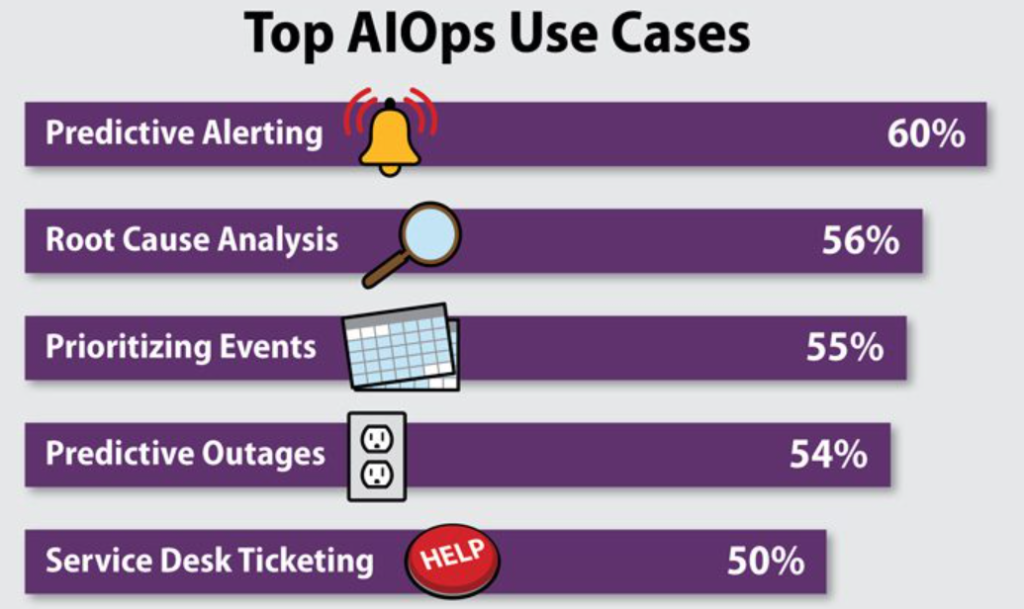
5 AIOps Use Case
The first AIOps use case is anomaly or threat detection. AIOps tools are valuable contributions to the making of a strong security management posture. Established processes and algorithms sift through traffic data to identify any botnets, scripts, or other threats that can take down a network. This can be incredibly helpful since many threats are complex, multi-vector, and unique. AIOps leverages machine learning to expose patterns that can undermine business service availability.
6. AIOps Use Case
The next AIOps use case is event correlation. Infrastructure teams are faced with numerous alerts when only a handful really matter. AIOps identifies the important alerts, groups them together using inference models, and identifies the core root causes of the problem. This means your infrastructure teams will no longer have overloaded inboxes filled with alert emails and get the one or two notifications that really matter instead.
7 AIOps Use Case
The third AIOps use case is intelligent alerts and escalation. After issues are identified by root cause alerts, ITOps teams leverage artificial intelligence to automatically notify subject matter experts or incident response teams to quickly resolve the problem. Artificial intelligence starts the remediation process prior to anyone even getting involved. Many AIOps tools continuously monitor hardware using machine learning to predict errors based on previous and real-time data prior to its occurrence. A ticket with all the necessary details on how to resolve the issue is automatically sent to inform you of the issue.
8 AIOps Use Case
The fourth AIOps use case is incident auto-remediation. AIOps is used as an end-to-end bridge between IT service management and IT operation management tools. IT service management teams traditionally sift through infrastructure data to identify and resolve root cause issues. AIOps understands the root cause through inference from infrastructure alerts and sends them to the IT service management team or tool through API integration pathways.
9 AIOps Use Case
The last AIOps use case is capacity optimization. This includes predictive capacity planning and references statistical analysis or AI-based analytics to optimize application availability and workloads across infrastructure. Capacity optimization continuously monitors raw utilization, bandwidth, CPU, memory, and others to increase overall application uptime.
- Anomaly Detection and Root Cause Analysis: AIOps can identify unusual patterns and anomalies in system behavior, helping IT teams quickly pinpoint the root causes of issues that could lead to downtime or performance degradation.
- Incident Management and Resolution: AIOps can automate incident detection, classification, and response. By analyzing historical data and real-time events, it can suggest appropriate actions or even trigger automated remediation workflows.
- Capacity Planning and Resource Optimization: AIOps can analyze historical data and predict future resource requirements, helping IT teams optimize capacity and resource allocation for better performance and cost-efficiency.
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization: AIOps can continuously monitor the performance of various IT components, such as servers, networks, and applications, and provide insights on how to optimize their performance.
- Change Management and Risk Assessment: AIOps can assess the potential impact of planned changes to the IT environment by analyzing historical data and simulating the effects of those changes.
- Incident Prediction: By analyzing patterns and historical data, AIOps can predict potential incidents before they occur, enabling proactive actions to prevent downtime or disruptions.
- User Experience Monitoring: AIOps can monitor the user experience of applications and services, providing insights into performance bottlenecks or issues that might impact end-users.
- Security and Threat Detection: AIOps can analyze security logs and events to detect suspicious activities, potential breaches, or security vulnerabilities, helping IT teams respond to threats more effectively.
- Log Analysis and Management: AIOps can analyze and categorize logs generated by various systems and applications, making it easier to identify important events and trends.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Management: AIOps can track and analyze metrics related to service level agreements, ensuring that the IT environment meets the defined performance and availability targets.
- Automated Remediation: AIOps can trigger automated workflows to resolve known issues, reducing the need for manual intervention and speeding up incident resolution.
- Incident Triage and Classification: AIOps can classify incidents based on severity, impact, and urgency, helping IT teams prioritize their responses.
- Predictive Maintenance: AIOps can predict when hardware components might fail based on historical data and usage patterns, enabling proactive maintenance to prevent unplanned downtime.
- Cloud Management and Cost Optimization: AIOps can provide insights into cloud resource usage, helping organizations optimize their cloud infrastructure for cost efficiency and performance.
- Network Monitoring and Troubleshooting: AIOps can monitor network traffic and detect anomalies, helping IT teams identify network issues and optimize network performance.
AIOps can be used for a variety of use cases, including:
- Anomaly detection: AIOps can be used to identify anomalies in IT data, such as spikes in CPU usage or memory utilization. This can help to identify potential problems before they cause outages or performance degradation.
- Root cause analysis: AIOps can be used to identify the root cause of problems. This can help to speed up the resolution of incidents and prevent them from happening again.
- Incident response: AIOps can be used to automate the response to incidents. This can help to reduce the time it takes to resolve incidents and minimize the impact on users.
- Proactive monitoring: AIOps can be used to proactively monitor IT systems for potential problems. This can help to prevent outages and performance degradation before they occur.
- Resource optimization: AIOps can be used to optimize the use of IT resources. This can help to reduce costs and improve performance.
- Compliance: AIOps can be used to help organizations comply with regulations. For example, AIOps can be used to monitor for security threats and compliance violations.
- Predictive maintenance: AIOps can be used to predict when equipment will fail. This can help organizations to schedule maintenance and avoid outages.
- Self-service: AIOps can be used to provide self-service tools to IT teams. This can help teams to troubleshoot problems and resolve incidents more quickly.

Leave a Reply